Embark on the ATP Photosynthesis & Cell Respiration WebQuest, an immersive exploration into the fundamental energy currency of life. Discover the vital role of ATP in photosynthesis, cellular respiration, and its multifaceted applications in biotechnology.
ATP, the adenosine triphosphate molecule, serves as the primary energy carrier in biological systems. This WebQuest delves into the mechanisms of ATP synthesis during photosynthesis and cellular respiration, highlighting their significance in the conversion and utilization of energy within cells.
ATP in Photosynthesis: Atp Photosynthesis & Cell Respiration Webquest
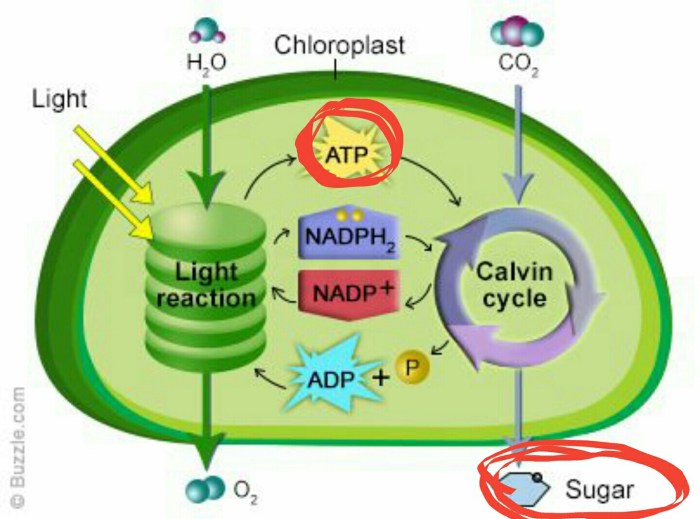
ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is a molecule that plays a crucial role in photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy. ATP is used as an energy currency within cells, providing the energy required for various cellular processes.
How ATP is Synthesized During Photosynthesis
ATP is synthesized during photosynthesis through two main processes: photophosphorylation and substrate-level phosphorylation.
- Photophosphorylation:This process occurs in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts and utilizes the energy of light to generate ATP. Light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll and other pigments, which excite electrons and transfer them through an electron transport chain. The energy released by the electron transport chain is used to pump protons across the thylakoid membrane, creating a proton gradient.
The proton gradient drives the synthesis of ATP through an enzyme called ATP synthase.
- Substrate-level phosphorylation:This process occurs in the stroma of chloroplasts and involves the transfer of a phosphate group from a substrate molecule to ADP, resulting in the formation of ATP. In photosynthesis, substrate-level phosphorylation occurs during the Calvin cycle, where carbon dioxide is fixed into glucose.
Importance of ATP for Photosynthesis
ATP is essential for both the light-dependent and light-independent reactions of photosynthesis.
- Light-dependent reactions:ATP is used to provide the energy required for the electron transport chain and the pumping of protons across the thylakoid membrane.
- Light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle):ATP is used to provide the energy for the fixation of carbon dioxide and the reduction of NADP+ to NADPH.
ATP in Cellular Respiration
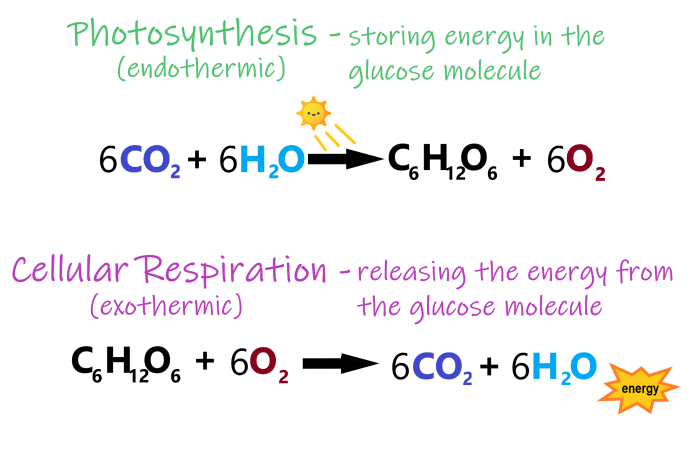
Cellular respiration is the process by which cells obtain energy from organic molecules, such as glucose. ATP is a central molecule in cellular respiration, acting as an energy currency and facilitating the transfer of energy between different cellular processes.
How ATP is Synthesized During Cellular Respiration, Atp photosynthesis & cell respiration webquest
ATP is synthesized during cellular respiration through three main processes: substrate-level phosphorylation, oxidative phosphorylation, and chemiosmosis.
- Substrate-level phosphorylation:This process occurs in the cytoplasm and involves the transfer of a phosphate group from a substrate molecule to ADP, resulting in the formation of ATP. In cellular respiration, substrate-level phosphorylation occurs during glycolysis and the Krebs cycle.
- Oxidative phosphorylation:This process occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane and involves the transfer of electrons through an electron transport chain. The energy released by the electron transport chain is used to pump protons across the mitochondrial membrane, creating a proton gradient.
The proton gradient drives the synthesis of ATP through an enzyme called ATP synthase.
- Chemiosmosis:This process refers to the mechanism by which ATP is synthesized through the movement of protons down the proton gradient created by oxidative phosphorylation.
Importance of ATP for Cellular Respiration
ATP is essential for the three main stages of cellular respiration:
- Glycolysis:ATP is used to phosphorylate glucose and other molecules, preparing them for further breakdown.
- Krebs cycle:ATP is used to phosphorylate substrates and drive the reduction of NAD+ and FAD to NADH and FADH2.
- Electron transport chain:ATP is synthesized through oxidative phosphorylation and chemiosmosis, utilizing the energy released by the electron transport chain.
Comparison of ATP Production in Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are two essential processes that utilize ATP as an energy currency. While both processes involve the synthesis of ATP, there are some key differences in the mechanisms and locations of ATP production.
Similarities
- Both photosynthesis and cellular respiration use ATP as an energy currency.
- Both processes involve the transfer of electrons through electron transport chains.
- Both processes utilize chemiosmosis to synthesize ATP.
Differences
- Source of energy:Photosynthesis uses light energy, while cellular respiration uses chemical energy stored in organic molecules.
- Location:Photosynthesis occurs in chloroplasts, while cellular respiration occurs in mitochondria.
- Products:Photosynthesis produces glucose and oxygen, while cellular respiration produces carbon dioxide and water.
Factors Affecting the Rate of ATP Production
- Light intensity:In photosynthesis, the rate of ATP production is directly proportional to the intensity of light.
- Substrate availability:In both photosynthesis and cellular respiration, the availability of substrates (e.g., glucose, oxygen) affects the rate of ATP production.
- Temperature:Both photosynthesis and cellular respiration are temperature-dependent processes, with optimal temperatures for maximum ATP production.
Applications of ATP in Biotechnology
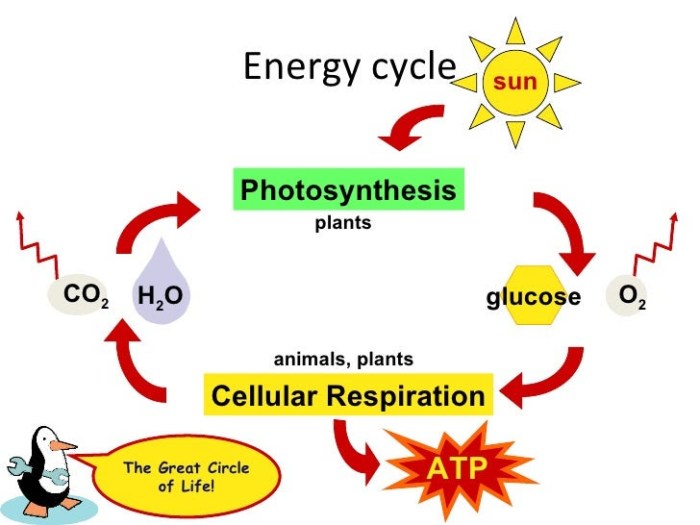
ATP is a versatile molecule with numerous applications in biotechnology, including:
Biofuel Production
ATP is used in the production of biofuels, such as ethanol and biodiesel. Ethanol is produced through the fermentation of glucose by yeast, and ATP is required for the phosphorylation of glucose and other substrates during fermentation.
Pharmaceutical Production
ATP is used in the production of pharmaceuticals, such as antibiotics and vaccines. ATP is required for the phosphorylation of nucleotides, which are essential components of DNA and RNA.
Other Applications
ATP is also used in various other biotechnology applications, including:
- Gene sequencing:ATP is used to provide the energy for the polymerase chain reaction (PCR), a technique used to amplify DNA.
- Protein synthesis:ATP is used to provide the energy for the ribosome during protein synthesis.
- Cell culture:ATP is used to provide the energy for cell growth and proliferation in cell culture.
Question Bank
What is the primary function of ATP in cells?
ATP serves as the primary energy currency, providing energy for cellular processes such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, and chemical synthesis.
How is ATP synthesized during photosynthesis?
During photosynthesis, ATP is generated through photophosphorylation, a light-dependent process that utilizes the energy of sunlight to convert ADP to ATP.
What is the role of ATP in cellular respiration?
In cellular respiration, ATP is synthesized through oxidative phosphorylation, a process that involves the transfer of electrons through the electron transport chain.