Match the scenarios with the economic concepts they illustrate. – In the realm of economics, understanding the interplay between supply and demand, elasticity, market structures, government intervention, and behavioral economics is crucial. This exploration delves into these concepts, providing a comprehensive analysis of how they shape economic outcomes.
By examining real-world scenarios, we will uncover the economic principles at play, enabling us to grasp the complexities of market dynamics and their impact on consumers, businesses, and policymakers.
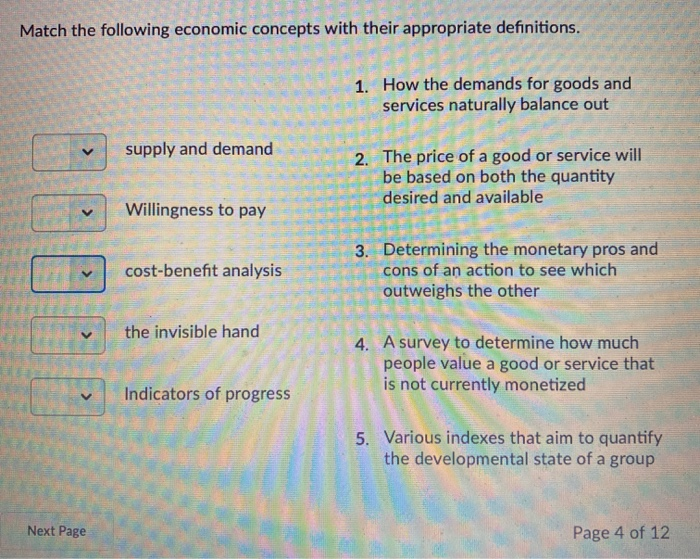
Supply and Demand
Supply and demand are fundamental economic concepts that explain how the interaction between buyers and sellers determines the prices and quantities of goods and services in a market. When supply and demand are in equilibrium, the market is considered to be in balance.
However, imbalances can occur when supply and demand are not equal. A surplus occurs when the quantity supplied exceeds the quantity demanded, leading to a decrease in prices to encourage buyers. Conversely, a shortage occurs when the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied, resulting in an increase in prices to attract more suppliers.
Shifts in supply or demand can also affect market prices. An increase in supply, with demand remaining constant, will lead to a decrease in prices. Similarly, an increase in demand, with supply remaining constant, will lead to an increase in prices.
Government intervention can be used to manage supply and demand imbalances. For example, price controls can be implemented to prevent prices from rising too high or falling too low. Subsidies can be provided to increase supply, while taxes can be imposed to reduce demand.
Elasticity
Elasticity measures the responsiveness of quantity demanded or supplied to changes in price. Price elasticity of demand measures the percentage change in quantity demanded in response to a 1% change in price. Similarly, price elasticity of supply measures the percentage change in quantity supplied in response to a 1% change in price.
Goods or services with elastic demand are highly responsive to changes in price, meaning that a small change in price will lead to a significant change in quantity demanded. Conversely, goods or services with inelastic demand are not very responsive to changes in price.
Elasticity has important implications for businesses and consumers. Businesses with products with elastic demand can increase revenue by lowering prices, while businesses with products with inelastic demand can increase revenue by raising prices.
Market Structures: Match The Scenarios With The Economic Concepts They Illustrate.
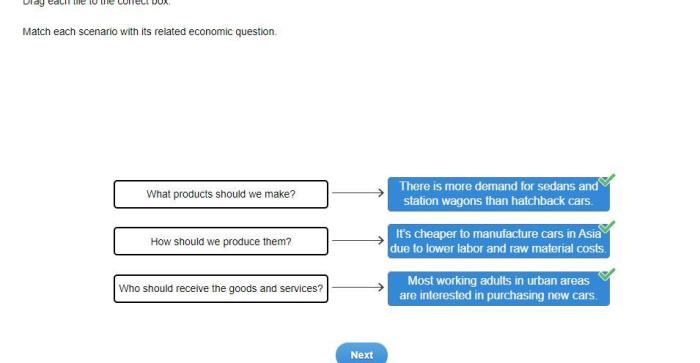
Market structures refer to the different types of market environments in which buyers and sellers interact. The main types of market structures are:
- Perfect competition: Many buyers and sellers, homogeneous products, and no barriers to entry or exit.
- Monopoly: One seller, no close substitutes, and barriers to entry.
- Oligopoly: A few dominant sellers, products may be differentiated or homogeneous, and barriers to entry.
- Monopolistic competition: Many sellers, differentiated products, and low barriers to entry.
Market structure impacts pricing, output, and consumer welfare. In perfect competition, prices are determined by the market and are typically lower than in other market structures. Monopolies have market power and can set prices above marginal cost, reducing consumer welfare.
Government Intervention
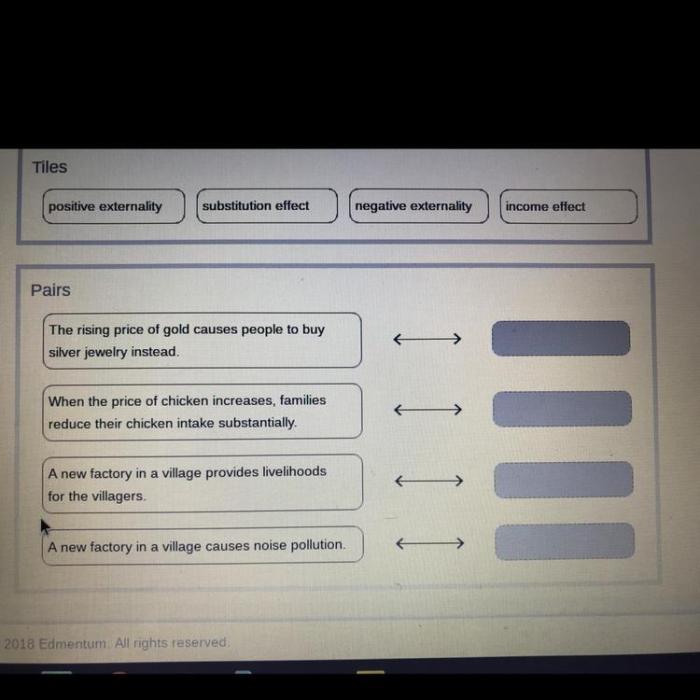
Government intervention in markets can take various forms, including price controls, subsidies, and taxes.
Price controls involve setting a maximum or minimum price for a good or service. Subsidies are payments made to producers to increase supply, while taxes are levied on producers or consumers to reduce demand.
Government intervention can affect market outcomes in several ways. Price controls can prevent prices from rising too high or falling too low, but they can also lead to shortages or surpluses. Subsidies can increase supply, but they can also be costly and inefficient.
Taxes can reduce demand, but they can also have negative effects on producers.
Behavioral Economics
Behavioral economics incorporates psychological factors into economic models. It recognizes that individuals do not always make rational decisions and that cognitive biases and heuristics can influence economic behavior.
Cognitive biases are systematic errors in thinking that can lead to irrational decisions. Heuristics are mental shortcuts that can simplify decision-making but can also lead to biases.
Behavioral economics has implications for public policy and business practices. By understanding how cognitive biases and heuristics influence behavior, policymakers and businesses can design interventions and strategies that promote rational decision-making.
Q&A
What is the significance of matching scenarios with economic concepts?
Matching scenarios with economic concepts allows us to connect abstract theories to real-world observations, enhancing our comprehension of how economic principles manifest in practice.
How can elasticity affect business strategies?
Understanding elasticity empowers businesses to optimize pricing, production levels, and marketing campaigns by anticipating consumer responsiveness to price changes.
What are the potential drawbacks of government intervention in markets?
Government intervention, while intended to address market inefficiencies, can sometimes lead to unintended consequences, such as market distortions, reduced competition, and stifled innovation.
